SGU Episode 398: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 381: | Line 381: | ||
=== Google Glass <small>(31:25)</small>=== | === Google Glass <small>(31:25)</small>=== | ||
http://www.google.com/glass/start/what-it-does/ | http://www.google.com/glass/start/what-it-does/ | ||
S: All right, Jay, let's move on. You're gonna tell us about Google glass. | |||
B: Yeah, baby. | |||
J: So, yeah, Steve, this is a real milestone. This is one of the pieces of technology that I've been waiting for for a long time. This is the beginning of real augmented reality. To give you a quick definition of what augmented reality is: so imagine a car mechanic that's wearing a pair of sunglasses and a computer is projecting onto the inside of those sunglasses a schematic so that the car mechanic is looking at the car engine and the computer's projecting say, the wiring system. So wherever he turns his head, the, it'll look like it's in 3D so he can see, or he or she can see things that aren't actually visible to the naked eye because the computer is laying that on top of reality. It's like another layer, or putting layers of information on top of reality. Or, a surgeon performing open-heart surgery would be able to see the heart in a 3D view unobstructed by the rest of the tissue surrounding it, or the rib cage, or whatever. You know, having that vantage point gives people the opportunity to achieve things much faster, more precisely and with much greater success overall. Now, I'm not saying that Google glass is offering that to us right now, but what Google is offering is the very first step in true augmented reality. So let me give you a quick list of the features of what it is, and I'll describe to you the actual component that you're wearing is, it's like taking a pair of sunglasses, removing the lenses and then on one side, on one eye, they'll put a, it's like a little module there that has a piece of glass that's hovering in front of one of your eyes. It'll project into your vision onto that piece of glass you're looking through that piece of glass, one of your eyes. It'll project a computer screen that looks like it's floating three or four feet in front of you, that doesn't have any borders or anything of course. And there's simply information there. You know, there's text, there's however, they're showing this information, it's gonna be a varying degree of different things. And you're gonna be talking to it. You're not gonna be using keyboard or a mouse or anything, that you're primarily gonna be using vocalization to turn it on, to tell it what you need it to do. And some of the features that it's launching with are it's gonna be able to record video. What you see, it's gonna record. It's gonna take pictures. You're gonna be able to start Google-Plus hangouts with people. You're gonna be able to search. You're gonna be able to also search photos, which is cool. You're gonna be able to do translations, you're gonna be able to get directions; you're gonna be able to use the Google Now software, which is like iPhone's Siri, where you can ask more complicated questions and actually tell it to do certain things, like take notes, put something in my address book, in my calendar, whatever. You can send messages to people and you can get flight, or there'll be a flight detail database attached, so you can call that up when you need it. You would start each command with "Okay, Glass," as if you were talking to someone. "Okay, Glass, I want you to start recording video right now." "Okay, Glass, stop recording video." The really cool thing about this though, is you take it with you, it connects into your iPhone or to your Android operating system, and it is based off of the Android operating system. And you wear it and you just put it on and you forget that it's there and it just becomes another interface for you. The big thing here is, guys, it truly is the beginning of the next way that we're gonna be interacting and experiencing reality. And it's going to be augmented by computers in a way now that we've really never experienced it before. We're all gonna be able to do things that we normally wouldn't be able to do, even simple things. Like let's say you went to Ikea and you bought a bookshelf. Everybody knows that directions that come from companies like Ikea or whatever, some are better than other, but for the most part having to construct something is a complete and total pain in the ass. This would be showing you what to do. It would be giving you visual cues using the actual things that you're looking at. Like, showing you what pieces connect to each other and where. | |||
B: And that's the key, Jay. To me that's the key. It's contextual information. It's not, you're not just surfing web pages. You are seeing overlays on reality and it knows what you're looking at, and gives you information based on your environment and what you're interacting with. And that's one of the reasons why this is gonna be so powerful. | |||
S: All right, Bob, Bob, what would be the porn application? | |||
J: Oh, my god. Don't even go there. | |||
B: God. Come on. | |||
J: Well, Bob's talking about what it will be like down the road, and | |||
B: I ''have'' to talk about that. | |||
J: Maybe a future use of this would be that you could tell Google glass "When I'm sitting at my work desk, I want my monitor to appear as if it's here where a physical monitor would be" but when you turn your head away, it stays in that three-dimensional space; you know, if you're looking at your computer monitor and you turn your head to the left, you don't see the monitor anymore, you wouldn't in real life. | |||
B: Exactly. | |||
S: Now let me be the wet-blanket skeptic. | |||
E: ''(laughing)'' I was gonna mention something about that. | |||
S: To bring things down a little bit. So everything that you guys are saying may come to pass at some point, but the thing that we have to keep in mind is that until we put this technology in the hands of lots of people, it's really hard to predict how people will want to use it. | |||
B: Oh, absolutely. | |||
S: And what it will be useful for. So all the things that you guys are speculating about, are speculation. So we don't know if this is going to be the smart phone, where everyone's gonna want to have 'em and it's gonna be much more useful than anyone ever thought, or if it's gonna be the Segue. You know, where it's not gonna be so revolutionary. But it'll have a niche where people use it for certain specific things, or, guys, remember the high-definition, high-frame rate situation where there just was something annoying about it, that people have a hard time adapting to. | |||
B: Ah, you're so full of it | |||
E: Yeah, adaptation. | |||
B: That's a horrible analogy. ''(laughter)'' Because this, this isn't, it's not a segue. People were gonna build cities around segue. That was a ridiculous prediction. It's not like a segue at all. This is an improvement on the computer interfaces. I mean computer interfaces, they're not going anywhere. That's a proven technology. It's just another way, it's another type of monitor, Steve. | |||
S: I know, Bob. I'm just saying, until people start using we won't know, it's like a video phone. We talked about the fact, oh video phones are coming. Well, why wouldn't you use a video phone? And it turns out that for a lot of things you don't wanna be looking at somebody. Why is texting so popular? The use of technology is hard to predict. | |||
B: I agree. | |||
== Who's That Noisy? <small>(38:06)</small>== | == Who's That Noisy? <small>(38:06)</small>== | ||
Revision as of 07:41, 14 April 2013
| This episode needs: transcription, links, 'Today I Learned' list, categories, segment redirects. Please help out by contributing! |
How to Contribute |
| SGU Episode 398 |
|---|
| 2nd March 2013 |
| (brief caption for the episode icon) |
| Skeptical Rogues |
| S: Steven Novella |
B: Bob Novella |
J: Jay Novella |
E: Evan Bernstein |
| Guest |
JR: Jon Ronson |
| Quote of the Week |
The world is much more interesting than any one discipline. |
| Links |
| Download Podcast |
| SGU Podcast archive |
| Forum Discussion |
| This episode is in the middle of being transcribed by banjopine (talk) as of {{{date}}}. To help avoid duplication, please do not transcribe this episode while this message is displayed. |
Introduction
You're listening to the Skeptics' Guide to the Universe, your escape to reality.
S: Hello and welcome to the Skeptics' Guide to the Universe. Today is Wednesday, February 27, 2013 and this is your host Steven Novella. Joining me this week are Bob Novella,
B: Hey, everybody.
S: Jay Novella,
J: Hey, guys.
S: and Evan Bernstein.
E: Ah. Kum bah wa, everyone.
B: Kum bah yay, what was that?
E: Kum bah ya, no. Kum bah wa. Japanese for good evening.
S: Good evening.
E: Lots of SGU listeners in Japan. We know a few.
S: So apparently Rebecca has some kind of phlegm situation going on.
E: I didn't know she was Amish.
S: We're trying to decide if she has the flu, whooping cough, or strep throat.
J: Well, get this, guys. So Rebecca emails us and says that she's not feeling well; that she woke up really late today, and she's been basically zonked all day. And at the same time, we have a little whooping cough scare going on over here with the newborn. This is what happened. My sister-in-law came to visit from Denver. And in the Midwest you know that the whooping cough incidences are higher and everything and I just didn't really think much of it other than everyone in the family got the tdap vaccination, which is the whooping cough
S: Did she and her family get the tdap?
J: Yeah, they did. What I found out today was that, like many of the vaccines that we get, you know they're guessing at which strain is gonna be the one that's gonna hit that year,
S: No, hang on a minute, Jay. What you're describing is relevant for the flu. With the whooping cough, it's not that there's like a different strain hitting every year, it's just that tdap covers only a very narrow number of strains and the virus has mutated. You know, it just, new strains are developing. But it's not like there's a seasonal strain like the flu. It's a little bit different.
J: Yeah, I didn't mean to confuse that. I know, like, exactly what you said, that there is a newer version of it that just wasn't covered by that particular vaccination that we got.
S: yeah.
J: So, her sister left on Monday morning. She called us up today, we're recording on Wednesday. She said "Guys, I had a bad cold on my way home, and now it's turning into something that's very, what I would consider to be whooping cough-like.
E: Yeesh.
J: So we called up our doctor, you know, I have a three-and-a-half-week-old in the house now, and you know, like, very dialed into this. And we called up the doctor up and me like "What's up? Like what do we do? What happens?" And pertussis is a bacteria, it's not a virus. So they have an anti-biotic for it.
E: Anti-biotic. Yeah.
J: So, what do you call it, Steve? Erythromycin?
S: Erythromycin, yeah.
J: Erythromycin, yeah. So that's the one that they use for it. And it's the mega-dose, like two pills the first day and then you take like this mega-dose thing for four days. Of course the baby's taking the liquid form and everything. But I'm sitting there tonight with my wife and we're giving the baby its first medication, and it's freakin' whooping cough medication! Like I wanted to strangle people. Thank you everybody for not . . .
S: Anyone who has never gotten vaccinated for whooping cough, yeah.
J: Something that we could
E: Way to blow the herd immunity; way to go.
J: We could get rid of it. Did you guys see the info-graphic of . . . the CDC puts out information every year, and somebody made an info-graphic of the incidence of morbidity before and after the vaccination for a particular disease came and went. Right?
S: Yeah.
J: And right out of the gate, things like smallpox and stuff, I don't remember the exact numbers, but we have certain diseases where there was like a half a million people dying a year, down to zero. After the vaccination. And there's like, in this info-graphic, I think there was more than a dozen of them. It was incredible. Like you see the numbers, how dramatically different they are. Right there. That's a hundred percent proof. They work. And yet people are walking around out there today and they don't care; that information is meaningless to them. How? Why?
B: Well what is the worst-case scenario with pertussis? I mean, how bad could it get?
J: It can kill you, Bob; it can kill a baby.
E: Death.
B: That's bad.
S: Yeah, there was that famous case in Australia where a baby caught, Dana McCaffery, caught whooping cough in a community that had very low vaccination rates because of the Australian anti-vaccination network preaching against vaccines, and, the baby caught it from unvaccinated people. And died. 'Cause the child was too young to be vaccinated. It's one of the populations that need to be protected by herd immunity.
This Day in Skepticism (4:33)
- March 2, 1983: Compact Disc players and discs are released for the first time in the United States and other markets. They had been available only in Japan before then.
S: Evan, so you're filling in for Rebecca this week for This Day in Skepticism.
E: I said "Good evening" in Japanese to start the show. And I did so because the compact disc, you guys remember what compact discs are, CDs,
S: They're still, they're still used today.
E: They are. Their first, most common usage was of course for music storage, right? Playing music. Put 80 minutes of uncompressed audio on one of those things. That's 737 megabytes of data. What do you think of that? So in Japan, is where the CDs were first, widely became available, in October of '82. However, on March 2nd of 1983, compact discs and their players were released for the first time in the United States and other markets around the world, whereas they'd only been available in Japan before but finally they came to the United States, and I remember this vividly. It was a big f'ing deal, for me and my 13-year-old friends and stuff who were all, in our own opinions, very big into music. And it was a rush to see who would get the first CD, who would be able to afford the first CD player. It was kind of bragging rights, in a sense. Do you guys remember?
S: Oh, yeah. Instantly replaced tapes, records; 8-tracks had already died by then.
E: Thank goodness.
S: Buy, yeah, and think about it, guys. Thirty years! And they're still a perfectly acceptable technology. I still buy CDs for music.
B: Really?
S: Sure.
B: Oh, man. I just download it all.
S: Yeah, but think about it. A CD, you can then rip it into any quality MP3 you want, which you own, without any DRM, and you have the CD for a backup. And it's still cost-effective. It's not like you're saving money by downloading. So it's still a perfectly viable technology. It's had a lot of longevity.
B: It's all right, I guess. I like, I hear a song that I like. Like, oh boy, that sounds really good. And I buy it. Within literally four minutes I have it on my iPhone and I'm listening to it. That's awesome.
S: I do that, too, but, if there's an album coming out and I know I want the whole album, I'll get it on a CD.
E: Something to remember, guys, is that when you purchase a CD, you're purchasing something physical that you actually own. And when you purchase a license to get a music or something you download through iTunes or something, there's a question, there's debates going on right now in the courts as to how much ownership do you actually have over that thing? In other words, can you put it into your estate and leave it to your heirs?
S: Right.
E: And they are fighting that. You know, the record industry, or industries, don't want those rights to be transferred on to descendents. Where, but with a CD you're guaranteed. That is yours, it's physical, you can do whatever the heck you want with it. So, keep that in mind also in the debate about, you know, what medium, what format you're gonna use for your music.
B: That's messed up.
News Items
Life Around Dying Stars (7:32)
http://phys.org/news/2013-02-future-evidence-extraterrestrial-life-dying.html#ajTabs
S: All right, well, Bob, talk about looking for life around dying stars.
B: If you insist.
S: I do.
B: So guys,
E: Like Mickey Rooney, are we talking? What are we talking here, dying stars?
B: Oh, boy. Guys, when you think of an extraterrestrial planet, especially one that supports life, what do you think of? Do you think of, you've got this planet orbiting a parent star that's kind of like our sun, right? Maybe it's a little bit bigger than our sun, maybe it's a little bit smaller. And of course, if that's the case, the habitable zone around the star changes because of how big and bright the star is.
S: Now, Bob, I think of Tatooine with two suns. (laughter)
E: Nice orchestral music playing.
S: Or Rigel 7 with a big planet in the distance with rings around it.
B: Yeah, but, still, it's like a, it's a real star, it's like a star that
S: Yeah, not a fake star.
B: It's fusing hydrogen into helium. No, but it's not a dead star, and that's the point here. There's a new theoretical study that finds that the most likely place possibly to find life on another planet may be around a dead star. More specifically, of course, a white dwarf. You know, I'm not talking about a neutron star or black hole. But not only that, they think they might be able to actually find one of these planets in the next ten years. Which seems like a pretty bold prediction.
E: But Bob, isn't a white dwarf after the star went through its initial sort of expansion then came back in on itself. Wouldn't it have kind of destroyed things on that
B: Well, exactly. And that's the huge problem. That's the first thing I thought of, well how can that be? A white dwarf is a dead star. It's a corpse of a sun-like star, at the end of its, you know in its old age it swells into a red giant and it totally crisps any of the planets that were nearby, but before it expels a lot of its mass, making the beautifully misnomered planetary nebula. So what's left is this collapsed core. It's about as big as the earth, but it's got the mass, it could have a mass of more than the sun. 1.4 solar masses, I think, is the ________________________ limit for that. So that's a lot of mass in a really tiny place. So clearly it's unbelievably dense, right? If you had a ton of white dwarf matter, if you could do that, you could fit it into a matchbox. I mean it's super, super tiny. You can thank the electron degeneracy pressure for that. But there's no nuclear reactions going on to produce energy, but because it's relatively small it could radiate it's remaining heat for literally billions of years. So clearly, then, this thing could have its own little Goldilocks zone to support life, even though it's really not even a star anymore. It's not creating energy, but it's just radiating away the energy that's contained in it for many, many, many eons. So then the next question then, Evan, which ties into your comment, was how does the planet get there, because the red giant's gonna wipe out anything that's nearby. Probably anything that's in the Goldilocks zone. So there's actually two ways that could happen. One might, you might predict, a planet can migrate in from the outskirts of a solar system; we've seen that with hot Jupiters: Jupiter-sized planets that have orbits closer than Mercury. How the hell did they get there? Well they can actually migrate in through the solar system. But there's another way. A planet can also form from the leftover dust and gas; and that, of course, would be a second-generation world, which I think is pretty cool. Now of course, though, this planet would have to get pretty damned close, since the heat source is so small and dim compared to regular living stars . . .
S: Bob, do we know that either of those can actually happen around a white dwarf, though?
B: The thing here, though, with this theoretical study, Steve, is that they ran these really sophisticated simulations and they've pretty much shown in the simulation everything that I'm talking about.
S: Okay. T B: That this can happen; they're incredibly confident that it could happen. They can think of no reason why it wouldn't happen. Now, it's not like every white dwarf is gonna have one these. They're saying that among the 500 closest white dwarves to the sun, they might find one or two that have planetary bodies in orbit around it that could support life. So, you know, one or two in 500 isn't great odds, but there's lots of stars and we can look at a lot of different things.
S: Yeah.
B: So, the interesting thing is, as you could imagine, these planets would have to be very close to the white dwarf in order to get enough heat to have liquid water and life evolve. So that turns out to be only about a million miles away, which is what one over ninety-three, wait, sorry. And that's, our orbit's 93 million miles, so it's way, way, way close to it. And it's year, of course, would only be about ten hours long, which is an amazingly fast orbit so that would, I cal . . .
E: That's a party every ten hours, oh my gosh.
B: I calculated Rebecca would be over 30,000 years old if she lived on that planet. (laughter) So, all right. So we've got this dead star that could conceivably keep a nearby planet warm enough for life, so we've got that. We've got a couple different ways for a planet to arrive or form nearby. So then the next interesting question is, how do we detect this thing? And, if you regularly listen to this show, I think you probably know: the transit method, right? A planet moves between us and their star. The output, the light output dips, and bam! You've detected a planet. Of course, it's a little bit more complicated than that, but that's essentially the idea. Now in this scenario it's actually even better. Now think of this system, though. You've got a planet real close to a white dwarf and the white dwarf is so tiny, I mean they could be comparable in size, so that when this planet eclipses the white dwarf, you're gonna have a huge dip in the light output. It would be an obvious signal. It would leap out and say "whoa!" This starlight almost completely disappeared.
S: But the plane of that system would have to be perfectly aligned with us.
B: Yes, it would have to be. But even if it wasn't, you could still occlude half the star or 33 percent, and that still would be really really good. That's not even the best part. The real icing on the cake for this is that the white dwarf emits so much less light it becomes much easier to determine the composition of the atmosphere of the planet in orbit around it. And it turns out that after the simulation I was talking about, they showed that after just a few hours of observation instead of something like hundreds of hours, we would know that the planet has perhaps water vapor or maybe oxygen in it. And oxygen would, that would be gargantuan news. That would be huge because, on earth anyway, oxygen is created by life. You take away life from the planet earth and it would slowly diminish, the oxygen would just disappear. It would dissolve into the oceans, it would oxidize the surface, and if we found a sizable amount of oxygen on a planet, I think it'd be pretty solid indication that there's probably some kind of life on the planet producing that oxygen. And if not, maybe it's some kind of alien machine that's creating and it wouldn't matter 'cause in that case we would find life anyway. So, either way, it's a win-win!
S: So now we've just gotta look for them.
B: Yeah, and the James Webb, the James Webb's a big thing, that once that guy comes online, that telescope comes online, I think, jees, I'm not sure when, but within a few years or so.
S: They plan on a 2018 launch date.
B: That is gonna have what it needs to really survey these white dwarves and find these planets and maybe find a planet that most likely has life on it. And how huge would that be; talk about the science story of the millennia, let alone the year!
S: Yeah, we'll probably cover that one.
B: Yeah, maybe. (laughter)
Ancient Lost Continent (15:06)
http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/science-environment-21551149
S: All right, well, Evan, I read
E: Yeah!
S: that geologists claim they have found a lost sunken continent.
E: You read correctly, Steve. And courtesy of the BBC, their headline reads "Fragments of ancient continent buried under the Indian Ocean."" So, what do you think? Is this it? They finally found Atlantis? Is the evidence incontrovertible?
S: It's in the Indian Ocean so it wouldn't be Atlantis, it would be Indiana.
E: Yeah, I suppose that would be more accurate.
B: No – Indianis.
S: Indianis
E: Indianis.
B: I kinda like it.
E: There are a few outlets out there; not exactly of BBC quality, with their own headlines, including "Fragments of ancient continent Atlantis found." And Atlantis is all in caps with an exclamation point and the word "found" is as well. And another one that says "Is this the real Atlantis?"
S: Nobody knows.
E: So, you know. Jees, that was not predictable at all that some people would be jumping all over the Atlantis part of the story. But, it has nothing to do with Atlantis whatsoever.
S: Zip. Zero. Nada.
E: Nada. Nope. This article's focus is on the study published in the journal Nature Geoscience. And like you said, Steve, the researchers have found evidence for the land mass that would have existed up to about 85 million years ago. Can I give you a quick little story to set this all up? So, a long time ago in a galaxy called the Milky Way, almost a billion years ago, and that was before iTunes and compact discs and vaccinations, on the earth there existed a super-continent. A super-continent is one very large continent. While at the same time, there are no other significant land masses anywhere on the earth. There have been many super-continents that have existed on the earth over the history of the earth.
S: A few.
E: Just a few. Well, about a dozen or so that they have listed online. But the super-continent from this particular period of time was called Rodinia. You guys may remember learning, I remember learning in grade school, about the super-continent called Pangaea, right?
S: Yeah. The most recent one, yeah.
E: But,
B: And Gondwana land is the other one, right?
E: That one, Gondwanaland.
J: Was that Guanaland? What is that, made of bat poop? The whole island?
B: (laughing) Yeah.
E: Pangaea, about 300 million years ago. No, Rodinia was well before that, about 750, maybe 800 million years ago. So we're talking a long time ago. As far as this particular new land mass that was discovered goes: picture in your mind a world map, and look in your mind for the country India. Okay? And then, to the south, the island nation of Madagascar. All right. Well, these areas were once connected, a part of Rodinia, and they were smashed up right next to each other. And researchers believe they've found evidence of a sliver of a continent known as, well they call it a microcontinent, that was once tucked between these two masses. But not only have they found the evidence, they're already calling it something. They're calling it Mauritia, named after the tiny island of Mauritius, which is the place where they actually discovered the evidence. So what kind of evidence did they find? Well, they collected samples from a volcanic eruption that took place estimated 9 million years ago, and within the samples of those sands and grains that they took in, were mixed in some much older minerals. They uncovered zircons. Now, zircons are known in geological circles for being found on the continental shelf and they are very, very old. These particular zircons that they found are estimated to be at least 600 million years old. And I read some estimates in some places that they could be almost 2 billion years old. The nearest known outcrop of continental crust that could have produced these zircons is on, well, Madagascar. But it's still very far away. And it's unlikely, they're trying to come up with scenarios by which, how could these zircons have gotten there by other means? They think that this is evidence for a land mass that actually, you know, believes a microcontinent that actually exists out there below the Indian Ocean. And they're going to be doing more studying about it. They're hoping to do more research and being a more detailed mapping of the floor of the Indian Ocean, and continue this research and try to find the sunken continent.
S: Yeah. I read the paper itself, and I think what they demonstrated is pretty solid. But the notion that the source of these grains of sands that they examining is this sunken microcontinent that existed between India and Madagascar. That's really just a hypothesis at this point. It's not like they're found the continent or they're proven that it exists. It's just that it would be one possible explanation for why this ancient zircon would be where it is. It sounds plausible, sounds like a reasonable story, but again, I think just a hypothesis.
B: In this context you always hear them saying "lost" or "sunken" continent. What the hell does "sunken" mean in this context?
S; Below the water. (laughter)
B: Well, yeah, but
E: You're right, Bob, it's a mystery.
B: What's the mechanism? I mean, is it just erosion, like the islands near Hawaii that have been eroded into the sea after they moved off of the volcanic hot spot? I mean, or would some cataclysm happen that actually made it, that shifted the crust and made it sink because of that? I mean . . .
S: Yeah, I think it's more to do with when two land, a land mass breaks apart into two land masses, the piece in, you know, there may be some of it in between the two pieces that breaks apart and sinks under the ocean. That's essentially what they're saying. Just the way the crust broke apart. One interesting thing about the whole supercontinents, et cetera, is that we're still not really sure why continents even exist.
J: Why? What do you mean? We don't know why they're there?
S: Actually what happens with plate tectonics is you have, the oceans are constantly turning over like a conveyor belt. So no part of the ocean is any older than a couple hundred million years. Parts of the ocean diving down below a continental plate, and you have rifts in the middle where new ocean floors emerging and spreading. Yeah, so you have this spreading zone and then subduction zone. But the continents are always floating on top of these oceanic plates. So how did that happen in the first place? Once it established itself to be that way, then you could see how it's self-perpetuating. But we're not really sure how that happened to begin with. Which is interesting.
B: Yeah, that's cool.
E: It is interesting.
S: The other thing that's interesting is the result of that is that continents are ancient. That's why stuff that's ancient has to be continental, right, 'cause anything from the ocean can only be a couple hundred million years old. If something's a billion years old, it had to come from a continent. Only the continents are that old.
E: Yes. Right, right. That's why the zircon's important.
S: Which is kind of nice. 'Cause if the continents were also occasionally diving underneath other plates and recycling, there wouldn't be fossils.
E: Yeah. We'd lose a lot of information.
S: Yeah.
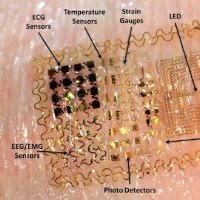
Electronic Tattoos (22:36)
S: All right. Let's move on. I'm gonna talk about electronic tattoos.
B: What the hell's that about?
S: Yeah.
E: Oh, it has something to do with Fantasy Island.
S: Here's the headline. You guys tell me what you think about this. "Temporary tattoos could make electronic telepathy possible."
E: Telepathy!
(garbled comments)
S: I know, I know. If somebody didn't send this to me, I would have used it as a Science or Fiction item.
E: Sorry!
S: Evan, you sent me several things I was gonna use for Science or Fiction. But anyway,
E: Oh, I undermined you totally.
S: This would have, I would have had Bob going. It's like "Now you're talking about telepathy??" (laughter) But, yeah. No. No telepathy. So what the technology is is they're essentially flexible electronics that you can apply to skin. And because they're flexible they could move around, they could bend. They're very thin, and they can serve a few functions. One primary function would be that they would essentially be an electrode. No big deal. So it could pick up electrical signals from the skin. So for example, if placed on the scalp, they could detect brain waves. But because this is, like, an electronic circuit, it's not just a dumb electrode, it's an actual circuit, you can build other functionality into it, including a transmitter to transmit signals to, say, a device. It could be used as very small, thin, flexible monitors. And so the technology seems very practical, very useful. I'm sure that this kind of thing is going to find a lot of applications. What I found amusing, maybe irritating, was the reporting of this technology, this, these devices in terms of what the possible applications would be. Because these are electrodes, that could read electrical signals from the brain, they started speculating wildly about the most advanced applications of the brain machine interface. Now we've chatted about this too, but I mean, that's something that would be far enough in the future we cannot say how long it's going to be; that we cannot extrapolate. The brain machine interface we have now are actually very good at, and getting better, at reading movements. So because we can map out the motor strip, you know, the motor cortex, and you know, you can put a lot of electrodes along the motor cortex and then people can learn how to use a robotic arm, for example, just by thinking about what they want it to do because it's interpreting the signals in their motor cortex. So that's about where the technology is now. But telepathy would require being able to read somebody's thoughts. And there the limiting factor isn't the electrodes, you know, it's not the signal.
B: It's the brain in the skull.
S: It's interpreting, although even if you had brain surface electrodes that were in incredibly high fidelity reading the EEG, the electrical signals from the brain, we still wouldn't know how to translate it into thoughts.
J: Yeah, how do you turn thought into a digital signal? What's the interpretation? And everybody's would be different. That's the real problem.
S: Well you'd have to calibrate, you know. And partly the machine would have to calibrate to you but also the user could learn how to use it, you know. But this will not allow for telepathy. That's the bottom line. This doesn't really get us any closer to telepathy.
E: But the headline! Look at the headline!
S: The researchers admitted that brain surface electrodes would work better than these. These skin surface electrodes are probably never going to have the fidelity, the discrimination, to be able to read thoughts.
J: Yeah. It just makes more sense that they, let's say they surgically implant something that is the analog to digital interface for the brain, then it transmits it to another device and let all the computer power happen somewhere else. It doesn't have to happen on the surface of your skin.
S: Yeah, well that's what this would do, too. This would just read signals transmitted to your smart phone and then you could communicate through your smart phone or operate your smart phone with thoughts alone.
E: Like, if I were to think, dial my home number. It would activate the phone to do something like that?
S: We're not at that point yet with this. But this could be useful for, like, paraplegic people who want to control a computer screen, or control a robotic device. Because these are very thin and small you could probably have a lot of them. But still, the signal is not as clear as the brain surface's invasive electrodes. So it remains to be seen how much utility these would have. But because these are, the advance here, is that the electrodes are integrated with other elements, such as transmitters, and that they're thin and flexible. You know, so you can put a lot of them on the scalp. You don't have to wear this big massive cap or something that's very unwieldy. So, it does expand the number of possible uses, but it doesn't get over the problem of reading the EEG from the scalp, and therefore telepathy is not one of the applications of this technology in my opinion. However, having said that, they did bring up the notion of sub-vocalizations. Are you guys familiar with that?
J: Yes.
B: Yeah, yeah; that's cool stuff.
J: I don't think we've talked about it on the show, but we, off the show, have talked about it.
S: Yeah, so, when you are saying words inside your mind, you tend to move your face, tongue and throat muscles in the way that you would if you were speaking them, just much more subtly. And there's actually been some research; I looked; there's not a lot, but there is some published research looking at detecting with skin surface electrodes, the muscle movements in the throat and the face and interpreting these sub-vocalizations. I'm reading some conflicting things, though. You know, some reviews say that being able to go from detecting these sub-vocalizations to actual words has been elusive. But other studies claim that they've been able to distinguish a number of different words from the EMG signals. But it's possible from, a limited set of words, that they can then know which one of those words that the person was thinking. So that's, actually, though . . .
E: Interesting.
S: That is plausible and that may just be a matter of incremental progress, and these electrodes, so these tattoos, might apply to that technology. Right? So if you're using this as a way of detecting sub-vocalizations, and the detection and analysis algorithm get sophisticated enough, and the user may be able to learn how to do that. 'Cause you can, I was doing this before the show, I was just thinking to myself and paying attention to what I was doing. And then also tried to maximize my movement, my sub-vocalization movements. You know what I mean? Like you can deliberately accentuate them.
E: Can you shut them off entirely if you think about it? Or is it just so subtle that you really don't have that level of control over it?
S: Well in researching this I did find lots of websites, and even some published studies, looking at the question of suppressing sub-vocalizations in order to improve or increase your reading speed. 'Cause apparently the sub-vocalizations slow you down.
J: So to clarify, Steve, if words are going through my head; if I'm sitting here saying to myself, oh, I've gotta get up early tomorrow morning, or whatever it is, I am having some type of muscular reaction in my throat? Every time?
S: Yes.
E: If you're reading.
S: No, even if you're just thinking, words.
E: Even if you're just thinking the words!
S: You're saying the words in your head, you are sub-vocalizing those words. Yes.
E: Right. Okay.
S: But the question is just, can we detect and interpret those muscle movements with enough precision and discrimination that we could translate that into the words that are in your head, that you're thinking. And this could give you like a fake telepathy. Like a pseudo-telepathy. It's not really telepathy 'cause it's through actual muscle movements. But that could still be really powerful. It still could functionally be telepathy.
B: Oh my god, yeah.
S: It's really not telepathy. It's probably better termed silent communication.
J: Yeah, imagine the military being able to communicate with each other without having to make any noise.
S: Yeah. Or spies. Just it's silent communication. You can imagine dictating in a crowded room without having to speak aloud.
Google Glass (31:25)
http://www.google.com/glass/start/what-it-does/
S: All right, Jay, let's move on. You're gonna tell us about Google glass.
B: Yeah, baby.
J: So, yeah, Steve, this is a real milestone. This is one of the pieces of technology that I've been waiting for for a long time. This is the beginning of real augmented reality. To give you a quick definition of what augmented reality is: so imagine a car mechanic that's wearing a pair of sunglasses and a computer is projecting onto the inside of those sunglasses a schematic so that the car mechanic is looking at the car engine and the computer's projecting say, the wiring system. So wherever he turns his head, the, it'll look like it's in 3D so he can see, or he or she can see things that aren't actually visible to the naked eye because the computer is laying that on top of reality. It's like another layer, or putting layers of information on top of reality. Or, a surgeon performing open-heart surgery would be able to see the heart in a 3D view unobstructed by the rest of the tissue surrounding it, or the rib cage, or whatever. You know, having that vantage point gives people the opportunity to achieve things much faster, more precisely and with much greater success overall. Now, I'm not saying that Google glass is offering that to us right now, but what Google is offering is the very first step in true augmented reality. So let me give you a quick list of the features of what it is, and I'll describe to you the actual component that you're wearing is, it's like taking a pair of sunglasses, removing the lenses and then on one side, on one eye, they'll put a, it's like a little module there that has a piece of glass that's hovering in front of one of your eyes. It'll project into your vision onto that piece of glass you're looking through that piece of glass, one of your eyes. It'll project a computer screen that looks like it's floating three or four feet in front of you, that doesn't have any borders or anything of course. And there's simply information there. You know, there's text, there's however, they're showing this information, it's gonna be a varying degree of different things. And you're gonna be talking to it. You're not gonna be using keyboard or a mouse or anything, that you're primarily gonna be using vocalization to turn it on, to tell it what you need it to do. And some of the features that it's launching with are it's gonna be able to record video. What you see, it's gonna record. It's gonna take pictures. You're gonna be able to start Google-Plus hangouts with people. You're gonna be able to search. You're gonna be able to also search photos, which is cool. You're gonna be able to do translations, you're gonna be able to get directions; you're gonna be able to use the Google Now software, which is like iPhone's Siri, where you can ask more complicated questions and actually tell it to do certain things, like take notes, put something in my address book, in my calendar, whatever. You can send messages to people and you can get flight, or there'll be a flight detail database attached, so you can call that up when you need it. You would start each command with "Okay, Glass," as if you were talking to someone. "Okay, Glass, I want you to start recording video right now." "Okay, Glass, stop recording video." The really cool thing about this though, is you take it with you, it connects into your iPhone or to your Android operating system, and it is based off of the Android operating system. And you wear it and you just put it on and you forget that it's there and it just becomes another interface for you. The big thing here is, guys, it truly is the beginning of the next way that we're gonna be interacting and experiencing reality. And it's going to be augmented by computers in a way now that we've really never experienced it before. We're all gonna be able to do things that we normally wouldn't be able to do, even simple things. Like let's say you went to Ikea and you bought a bookshelf. Everybody knows that directions that come from companies like Ikea or whatever, some are better than other, but for the most part having to construct something is a complete and total pain in the ass. This would be showing you what to do. It would be giving you visual cues using the actual things that you're looking at. Like, showing you what pieces connect to each other and where.
B: And that's the key, Jay. To me that's the key. It's contextual information. It's not, you're not just surfing web pages. You are seeing overlays on reality and it knows what you're looking at, and gives you information based on your environment and what you're interacting with. And that's one of the reasons why this is gonna be so powerful.
S: All right, Bob, Bob, what would be the porn application?
J: Oh, my god. Don't even go there.
B: God. Come on.
J: Well, Bob's talking about what it will be like down the road, and
B: I have to talk about that.
J: Maybe a future use of this would be that you could tell Google glass "When I'm sitting at my work desk, I want my monitor to appear as if it's here where a physical monitor would be" but when you turn your head away, it stays in that three-dimensional space; you know, if you're looking at your computer monitor and you turn your head to the left, you don't see the monitor anymore, you wouldn't in real life.
B: Exactly.
S: Now let me be the wet-blanket skeptic.
E: (laughing) I was gonna mention something about that.
S: To bring things down a little bit. So everything that you guys are saying may come to pass at some point, but the thing that we have to keep in mind is that until we put this technology in the hands of lots of people, it's really hard to predict how people will want to use it.
B: Oh, absolutely.
S: And what it will be useful for. So all the things that you guys are speculating about, are speculation. So we don't know if this is going to be the smart phone, where everyone's gonna want to have 'em and it's gonna be much more useful than anyone ever thought, or if it's gonna be the Segue. You know, where it's not gonna be so revolutionary. But it'll have a niche where people use it for certain specific things, or, guys, remember the high-definition, high-frame rate situation where there just was something annoying about it, that people have a hard time adapting to.
B: Ah, you're so full of it
E: Yeah, adaptation.
B: That's a horrible analogy. (laughter) Because this, this isn't, it's not a segue. People were gonna build cities around segue. That was a ridiculous prediction. It's not like a segue at all. This is an improvement on the computer interfaces. I mean computer interfaces, they're not going anywhere. That's a proven technology. It's just another way, it's another type of monitor, Steve.
S: I know, Bob. I'm just saying, until people start using we won't know, it's like a video phone. We talked about the fact, oh video phones are coming. Well, why wouldn't you use a video phone? And it turns out that for a lot of things you don't wanna be looking at somebody. Why is texting so popular? The use of technology is hard to predict.
B: I agree.
Who's That Noisy? (38:06)
- Answer to last week: Whistlepig
Questions and Emails
"Ow!" (40:36)
- Why do we say, "Ow!"? Joe Shoults
Interview with Jon Ronson (44:20)
- Interview with Jon Ronson, recorded at CSICon 2012.
Science or Fiction (1:00:50)
Item number one. Scientists have developed an imaging system that can look through walls into a burning building and identify survivors that need rescuing. Item number two. A new analysis finds that Spiderman’s webbing would have been strong enough to stop the commuter trains as depicted in the Spiderman 2 movie. And item number three. Researchers discover a virus with an adaptive immune system.
Skeptical Quote of the Week (1:13:44)
The world is much more interesting than any one discipline.
Edward Tufte
Announcements (1:15:27)
References

|